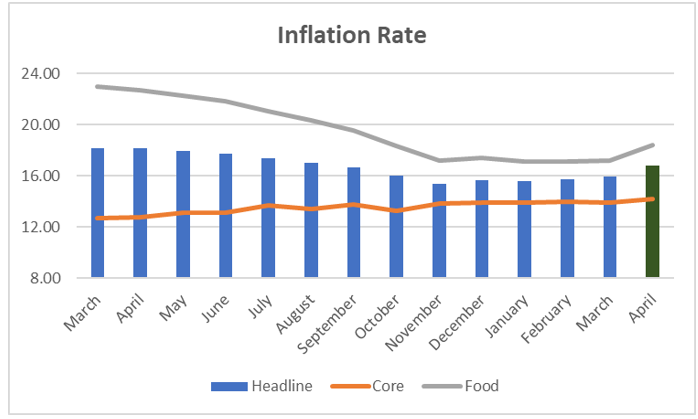
Nigeria’s Inflation Rate rose to an 8-month High of 16.82% in April 2022
We expect headline inflation to continue its upward trend in the coming months due to the supply disruptions that have ensued from the conflict in Eastern Europe which has left a mark on the local economy, given Nigeria’s dependency on imported energy and food. These factors will consequently lead to an uptick in the prices of goods and services. Also, FX pressures in the FX market will further fuel inflation expectations.
On the policy end, there is the possibility of an upward adjustment in the Monetary Policy Rate (MPR), in an attempt to keep the net foreign flows positive and also signal the monetary authority’s concern regarding inflation. However, the CBN could continue its current stance by judging that Nigeria’s inflation has a different set of drivers and as such may not respond to monetary policy decisions. Hence, we think the CBN would call on the fiscal authorities to address the structural impediments to food supply to contain higher prices. Therefore, we expect that at the next monetary policy committee meeting, the committee will hold the benchmark interest rate constant at 11.50% in order to continue to maintain post-covid economic recovery.