-
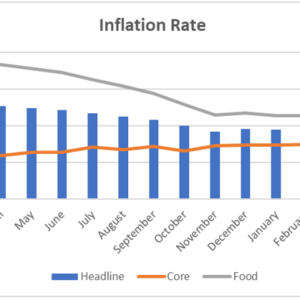
Nigeria’s Inflation Rate rose to an 8-month High of 16.82% in April 2022
We expect headline inflation to continue its upward trend in the coming months due to the supply disruptions that have ensued from the conflict in Eastern Europe which has left a mark on…
-
Aftereffect of the festive season Leads to a Marginal Slowdown in Inflationary Pressure
Looking further into the year, we recognize the possibility of upside inflation surprises, as the sub-par food harvests of last year could cause food supply to be slim during this year’s planting season,…
-
Maintaining PMS Subsidy Payments to Put more Pressure on Nigeria’s Fiscal Burden
The cost of the PMS subsidy rose from 4 percent of Federation oil and gas revenue captured by the NNPC in 2020 to 35 percent in 2021, an untenable fiscal burden for a…